If you’ve ever Googled something, you probably know how precise the search engine can be. However, what if you notice something odd when searching for the same phrase with slight variations? For instance, typing “googler.com owner” and “googler .com owner” into Google results in completely different outcomes. It’s fascinating how a simple space can lead to distinct search results. So, let’s explore why this happens and how Google’s algorithms handle these subtle changes.
A Small Change Makes a Big Difference
At first glance, it seems like adding or removing a space shouldn’t cause such a noticeable difference in the search results. However, search engines like Google are highly sensitive to every detail. When you type “googler.com owner” without any space between the word “googler” and “.com”, Google treats this as a single entity or domain name. This affects how the search engine processes and ranks pages. It’s like telling Google, “I’m looking for the owner of this particular website.”
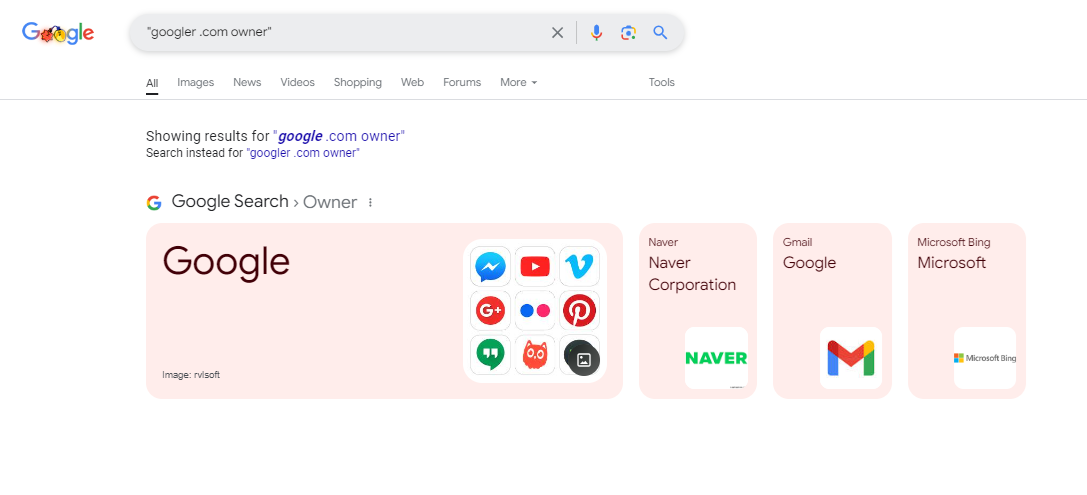
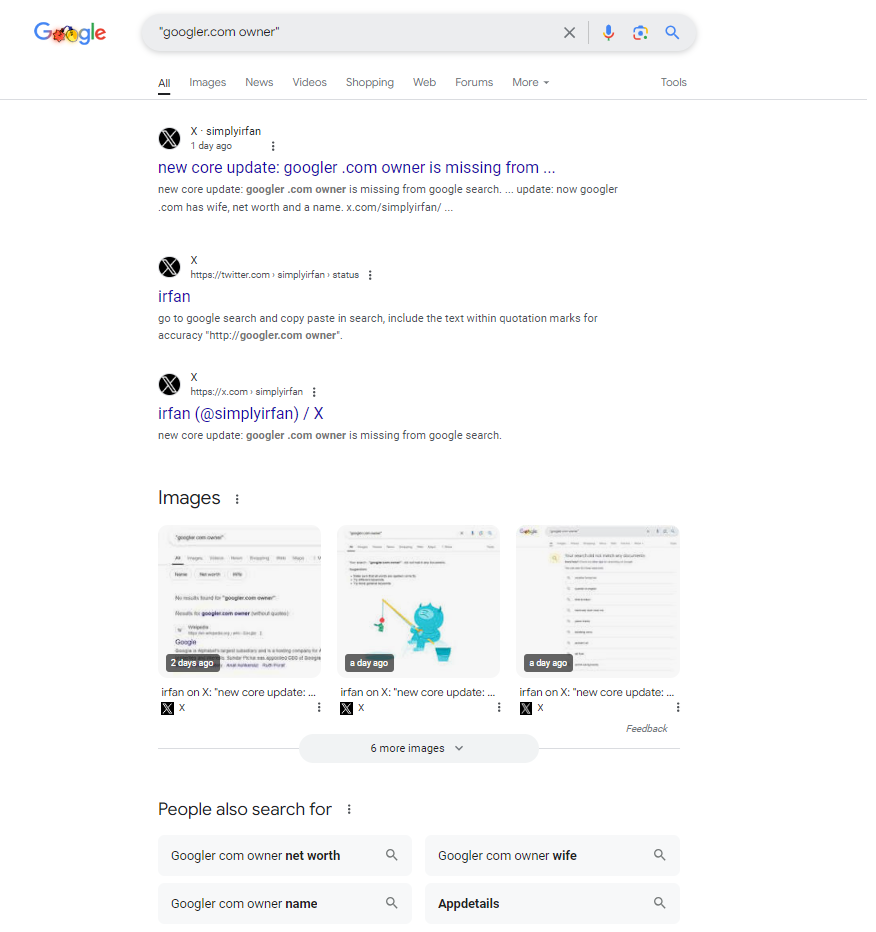
On the other hand, when you type “googler .com owner” with the space, Google interprets it differently. The space suggests a separation between the word “googler” and the domain extension “.com.” As a result, the algorithm may focus more on the individual term “googler” rather than treating it as a domain. This can change the search results drastically. Google might bring up results related to the term “googler” in general, like articles about Googlers (people working at Google), rather than the owner of a website.
Google’s Algorithms at Work
Google uses sophisticated algorithms to rank web pages. These algorithms consider multiple factors, like keywords, website authority, and even the tiniest punctuation marks. A space between words or characters can dramatically affect how results are shown. The search engine looks at the exact words you enter and determines what you’re likely searching for. Even a small difference in punctuation or spacing can lead Google to display different pages because it interprets the query differently.
In the case of “googler.com owner,” Google recognizes it as a specific domain name and looks for pages linked to the website. For “googler .com owner,” however, it might treat “googler” as a search term on its own and display results that refer to Google or the word “googler,” such as information about Google’s employees or the company itself. As a result, the results may be about something entirely different from what you intended.
Googler.com Is Owned by Google.com
Interestingly, “googler.com” is indeed owned by Google. The domain name is part of Google’s vast portfolio, and as with many other domain names they own, it’s likely registered for branding or internal purposes. Google frequently acquires various domain names to prevent them from being used by others or to direct traffic toward their brand. While “googler.com” itself may not be a well-known or widely advertised part of Google’s web presence, it’s clear that Google has ownership over it. This adds an extra layer of intrigue when searching for the “owner” of this domain, especially when the query results vary.
This fact also highlights how domain ownership works in general. While Google might own a site like “googler.com,” it doesn’t necessarily mean that the site is actively used for a service or public-facing content. In this case, Googler.com might not have much information on it for the public to see, which could be why results for “googler.com owner” can be limited or difficult to find.
Related: Google Gets Caught Red Handed in Site Reputation Abuse
Types of Variations in Search Operators
Google allows users to refine their searches with special operators that can change the results significantly. Here are a few common search operators and how they can alter search outcomes:
1. Quotation Marks (“”): When you search for a phrase in quotes, Google looks for that exact sequence of words in that specific order. For example, searching for “googler.com owner” with quotation marks tells Google you want results where this exact phrase appears, which will be different from a general search of those words.
2. Plus (+) and Minus (-) Signs: The plus sign can be used to include specific words in your search, ensuring they appear in the results. The minus sign excludes words. For example, searching for “googler +com owner” will force Google to look for results that mention “googler” and “com” together, while “googler -com” will remove results that mention “com.”
3. Wildcard (*): The asterisk can be used as a placeholder for any word. If you search “googler * owner,” Google will return results where any word can appear between “googler” and “owner.” This is useful for more general searches when you’re unsure of the exact phrasing.
4. Site Search (site:): If you’re looking for information from a particular website, you can use the “site:” operator. For example, “owner site:googler.com” will show results from the googler.com domain, but no other websites.
5. Related Search (related:): To find websites related to a specific domain, use “related:googler.com.” This will show websites that are similar to Googler.com, based on Google’s algorithm.
These search operators can change how specific or broad your search results are, allowing you to narrow down results based on your needs. Understanding how and when to use them can help you make the most of your search queries.
Recommended: Understanding Site Reputation and Google’s Spam Policies
Recommendations for Effective Searching
To get the best results from Google and avoid discrepancies like those seen with “googler.com owner” versus “googler .com owner,” follow these simple recommendations:
1. Be Specific: The more precise your search, the better the results. For example, adding the correct spacing or quotation marks can significantly improve the quality of your search results.
2. Use Search Operators: Utilize the search operators mentioned above to narrow down your search, especially when looking for specific information, like domain ownership or a specific term.
3. Check Your Spelling and Punctuation: Google takes punctuation into account, so even a misplaced space or comma can lead to vastly different results. Double-check your query for accuracy.
4. Use Synonyms: If your first search doesn’t give the results you need, try using different words that mean the same thing. For example, if “googler.com” isn’t yielding useful information, try “googler domain owner.”
5. Consider Context: If you’re after specific data, like the owner of a website, use the relevant terms in your query. Adding a specific question like “Who owns googler.com?” may give better results.
Glitches and Anomalies in Google Search
Despite its impressive power, Google’s search engine isn’t perfect. Occasionally, glitches and anomalies can cause unexpected behavior in search results. These glitches can be caused by many factors, including:
1. Indexing Errors: Sometimes, Google may fail to index a website correctly, leading to incomplete or inaccurate results. This could be why searching for “googler.com owner” might not return relevant information if the website’s ownership details haven’t been indexed properly.
2. Crawling Issues: If Googlebot (Google’s web-crawling bot) has trouble accessing a website due to technical issues (like broken links, server errors, or poor SEO), it might not display the correct results for queries related to that website.
3. Algorithm Updates: Google frequently updates its search algorithms. These changes can sometimes cause fluctuations in search results, including different outcomes when searching with slight variations in the query. These updates can also cause inconsistencies, especially if the algorithm update affects how it interprets certain words or punctuation.
4. Cache Problems: Google may show outdated search results due to its cached pages. If a website has recently changed ownership or content, but Google’s cache hasn’t been updated yet, the search results may not reflect the most recent information.
5. User Errors: Sometimes, the issue is on the user’s end. An extra space or incorrect spelling can lead to irrelevant results. Although Google works hard to predict what you’re searching for, it’s not always perfect.
Final Thoughts on Search Variations
In conclusion, the difference in search results between “googler.com owner” and “googler .com owner” illustrates the importance of precision in search queries. Google’s algorithm is designed to interpret every character, even spaces, which can drastically change what you see. While it might seem like a minor issue, understanding how these small differences affect search results can help you become a more efficient searcher.
Next time you’re typing a search query, pay attention to the details. A tiny adjustment, like adding or removing a space, could change the entire outcome of your search. Google’s ability to provide relevant results is impressive, but as users, it’s up to us to enter the right information. With the right tools and knowledge of search operators, you can unlock more accurate and tailored results, helping you find exactly what you need.