Google’s Site Reputation Abuse Policy is an essential set of guidelines that ensures search results stay relevant and reliable. It protects users from misleading or manipulative practices that could distort the search results. By promoting high-quality, trustworthy content, Google encourages website owners to follow ethical practices. Violating these guidelines can lead to serious consequences, affecting your website’s visibility and rankings. Let’s break down this policy and explore how it impacts both users and website owners.
Third-Party Content and Its Impact
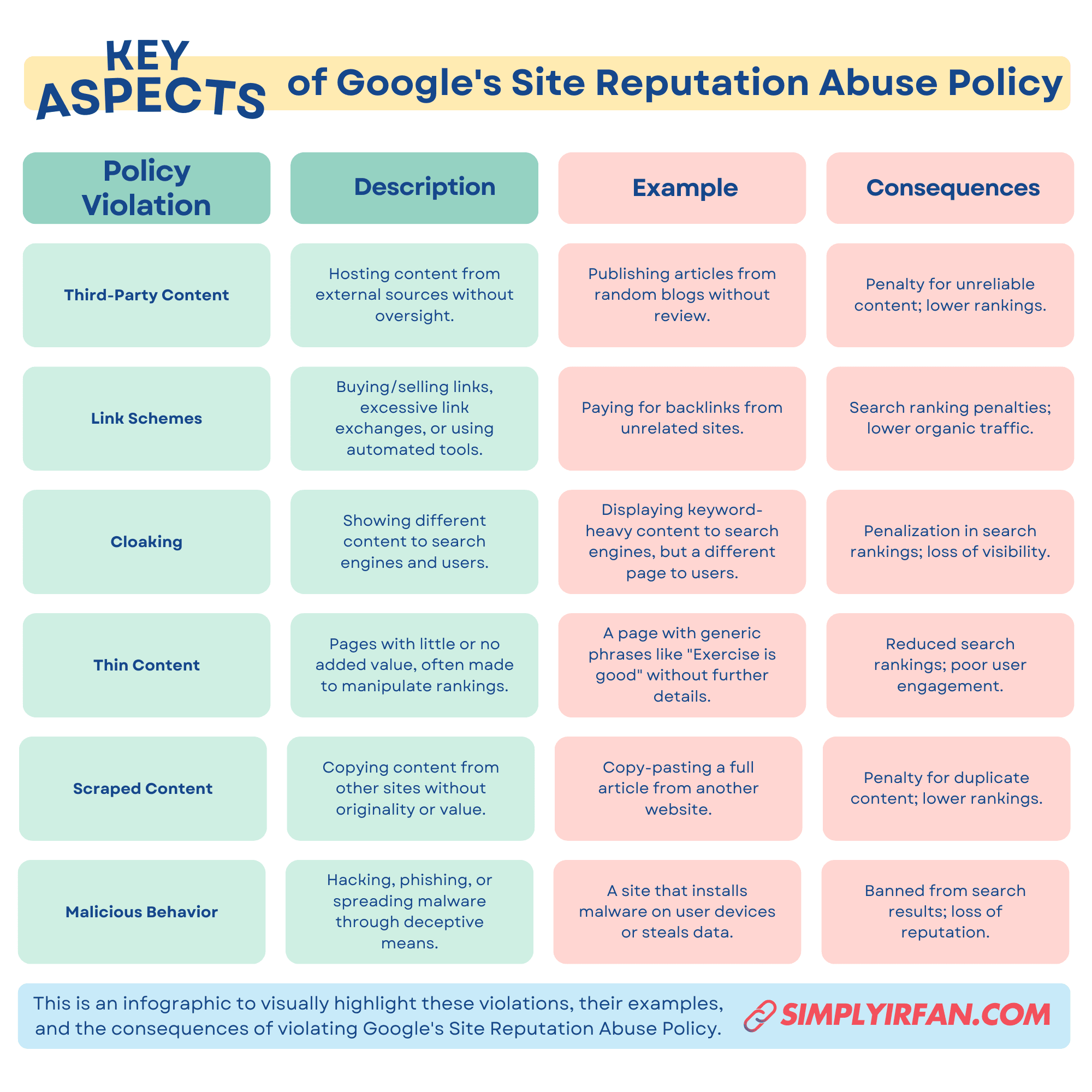
Google is particularly strict about third-party content. If a website hosts content from other sources without adequate oversight, it can be considered a violation. The intent behind this is clear: manipulative practices that aim to influence search rankings are not tolerated. Google wants to ensure that the content users see is trustworthy and valuable. Without proper control, third-party content can mislead both users and search engines, harming the website’s reputation.
Example: Imagine a website that publishes several articles about health tips, but the content is sourced from various random blogs with little to no review or fact-checking. If these articles are misleading or manipulative, they can harm the website’s reputation. Google may penalize such sites, as the content is seen as lacking credibility and not closely managed, potentially affecting the site’s search rankings. Proper control over third-party content ensures quality and reliability, helping maintain a site’s trustworthiness.
Link Schemes and Their Consequences
Link schemes are another critical aspect of this policy. Buying or selling links, engaging in excessive link exchanges, and using automated tools to generate links are all considered manipulative practices. These activities may seem like shortcuts to improve a website’s search ranking, but they ultimately harm the overall search ecosystem. Instead of focusing on quality, websites engaging in link schemes try to manipulate the system. This goes against Google’s goal of delivering authentic, user-focused content.
Example: Let’s say a website offering vacation packages buys links from various unrelated blogs. While this might temporarily boost rankings, Google sees this as a violation of its guidelines. As a result, the website could be penalized, causing its rankings to drop and leading to a decrease in organic traffic. Google prefers natural, relevant backlinks earned through quality content, not through manipulation.
Cloaking: The Hidden Threat to Transparency
Cloaking is another deceptive technique that Google specifically targets. This happens when a website shows different content to users and search engines. For example, a website might display one version of content to search engine crawlers, and another to visitors. This practice misleads search engines about the true content of a site and manipulates rankings. Google’s algorithm is designed to detect cloaking and penalize sites that use it. This helps maintain transparency and ensures users find what they’re looking for.
Example: Imagine a website about “best laptops” that hides its true content from users, but shows a keyword-stuffed page full of laptop specifications to search engines. This misleads both users and search engines, violating Google’s guidelines. If detected, the site could face penalties, leading to a drop in its search rankings and credibility.
Thin Content: Content Without Value
Creating “thin content” is another violation of Google’s policy. Thin content refers to pages with little or no added value. These pages are often created with the sole purpose of ranking higher in search engines. However, Google values quality content that provides real value to users. Websites with thin content may attract visitors in the short term, but they won’t hold attention or provide any meaningful information. Over time, this type of content can harm the website’s credibility and rankings.
For example, a blog post titled “Best Tips for Fitness” that only contains a few generic sentences like “Exercise is good for health” and “Eat healthy food” would be considered thin content.
This type of page lacks depth, detail, and originality, offering no real value to the reader. Google may penalize such content, lowering its search ranking since it doesn’t effectively answer users’ queries or provide substantial information.
Scraped Content: A Shortcut That Doesn’t Work
Scraped content is when a website uses content from other sites without adding any originality or value. Copying text or images without permission doesn’t contribute anything new to the internet. Google rewards original, informative, and helpful content, while penalizing scraped content. This policy ensures that websites that steal others’ work don’t get a free pass. Instead of relying on scraped content, website owners should focus on creating unique material that benefits their audience.
For example, a website might copy an entire article from a popular news site, pasting it on their own page without any new insights or commentary.
While this might seem like an easy way to get content, Google can detect scraped material. Websites that rely on this tactic risk penalties, including lower search rankings, because Google prioritizes original, high-quality content that adds value to users.
Malicious Behavior and Its Serious Consequences
Google also has a strict stance on malicious behavior. This includes hacking, phishing, or using deceptive methods to spread malware. Websites engaging in such practices not only violate Google’s policy but also put users at risk. Google aims to protect users from security threats and provide a safe browsing experience. Malicious activities harm the internet’s ecosystem and erode trust in websites.
For example, a website might appear legitimate but secretly install malware on visitors’ devices or steal personal information through phishing.
Such behavior not only violates Google’s guidelines but also puts users at serious risk. If Google detects this, the website can be banned from search results, leading to a loss of visibility and trust. Websites engaging in malicious activities face severe penalties and significant damage to their reputation.
Related: Google Site Reputation Check… and Fails the Site Reputation Test
Goals of the Site Reputation Abuse Policy
The primary goal of this policy is to promote relevant, trustworthy, and user-focused content. By penalizing manipulative practices, Google ensures that search results are fair and valuable. Websites that focus on high-quality content will naturally rise in rankings, while those attempting to deceive the system will be penalized. Ultimately, this policy helps create a better experience for internet users, who can trust that the results they see are credible and valuable.
Penalties for Violating the Policy
Websites found violating these guidelines can face severe penalties, including manual actions. These penalties can significantly hurt a website’s search rankings, leading to a decrease in organic traffic. For many websites, this means a drop in visibility and potential revenue. A manual action can take time to resolve, and during this period, a site’s search rankings may be severely impacted.
Conclusion: Why Following the Policy Matters
Google’s Site Reputation Abuse Policy is crucial for maintaining a healthy and trustworthy internet. By adhering to these guidelines, website owners ensure that their content remains valuable and relevant to users. Manipulative practices like link schemes, cloaking, and scraped content only lead to short-term gains but ultimately harm a website’s reputation. Instead, focusing on creating original, useful content will yield better results in the long run. Staying aligned with Google’s policies will not only protect your site’s rankings but also contribute to a positive online experience for everyone.