WordPress powers more than 40% of the web. That means almost half of the websites you visit daily—blogs, business sites, online stores, portfolios—are running on it. But for many people starting out, the question is simple: how does WordPress actually work?
This guide answers that step by step, while also exploring themes, history, plans for bloggers, common issues like speed, and what the future holds. Whether you’re just curious or ready to launch your own site, this breakdown will give you a clear picture.
Contents
WordPress Step by Step: From Install to Launch
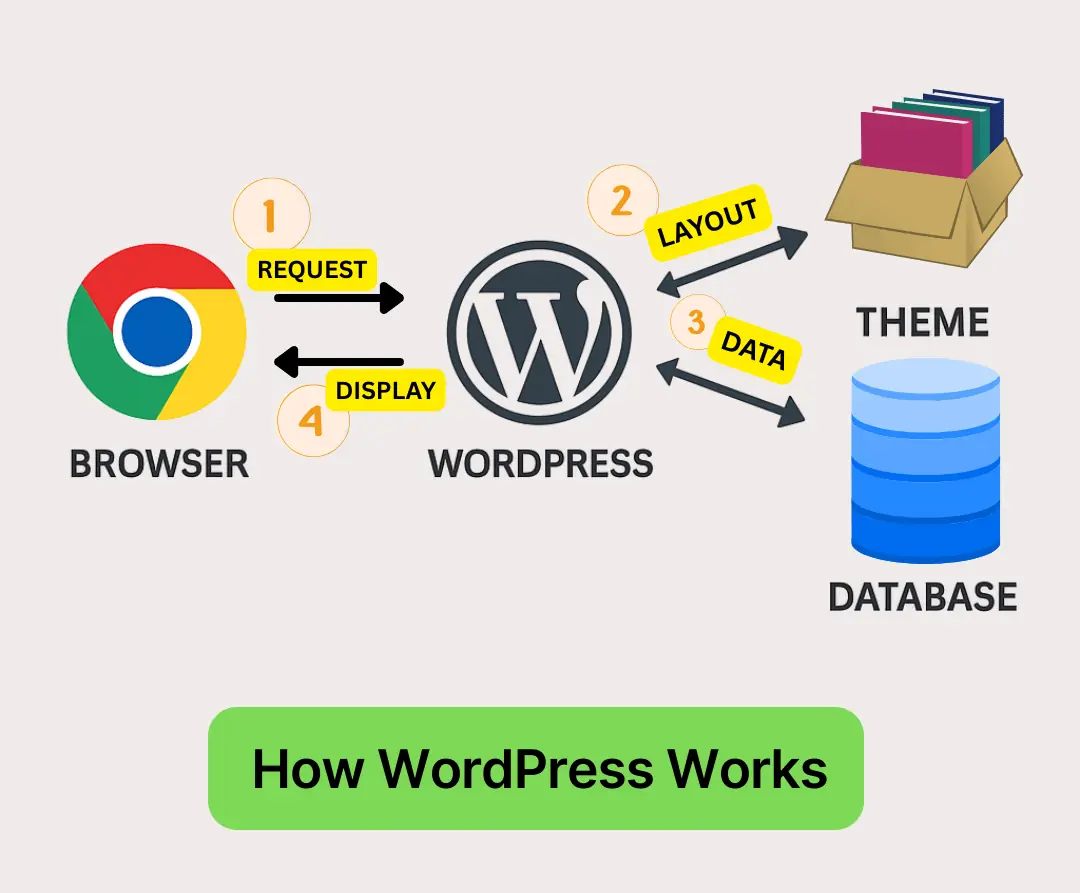
Let’s start at the beginning. If you’re wondering how WordPress works, the process is straightforward once you see it broken into steps. Think of WordPress as the “engine” of your site. You add fuel with content, dress it up with a theme, and fine-tune it with plugins. Here’s how the journey unfolds:
1. Pick Your Version: WordPress.com or WordPress.org
The first decision you face is whether to use WordPress.com or WordPress.org. Both share the same core software, but they offer different experiences. WordPress.com is a hosted service. You sign up, pick a plan, and the technical details like server management, updates, and security are handled for you. It is the simplest path for beginners who want to start writing or publishing quickly without thinking about hosting.
WordPress.org, on the other hand, is the self-hosted version. You download the software for free and install it on your own hosting plan. This gives you total control over your website. You can install any plugin, use custom themes, and even edit the code directly if needed. The tradeoff is that you are responsible for updates, backups, and security.
So which one should you choose? If you want convenience and do not mind some limits, WordPress.com is a safe starting point. If you want full flexibility, advanced customization, and the ability to monetize without restrictions, WordPress.org is the better choice. Both options give you the same foundation, but your long-term goals should guide your decision.
2. Secure Your Domain and Hosting
If you go with WordPress.org, the next step is getting a domain and hosting. A domain is your website’s address, like www.example.com. Hosting is the service that stores your site’s files and makes them accessible on the internet. Without hosting, your site has no home.
Choosing a good host matters. Cheap, overcrowded servers can make your site slow or unreliable. Look for providers that specialize in WordPress hosting. Many offer automatic updates, built-in caching, and dedicated support. Popular options include Bluehost, SiteGround, and Kinsta. Prices range from a few dollars a month to premium plans for high-traffic sites.
Domains can be purchased directly from hosting providers or through registrars like Namecheap and GoDaddy. Try to keep your domain short, easy to remember, and relevant to your brand. Once purchased, connect your domain to your hosting account so it points visitors to your WordPress installation.
Think of it this way. The domain is your street address, the hosting is the land, and WordPress is the house you are about to build. Choosing the right land and address sets your site up for long-term success.
3. Install WordPress
With your domain and hosting ready, it is time to install WordPress. Fortunately, most hosting companies make this process simple. Many offer one-click installation from your account dashboard. With a few clicks, the software is installed and ready to use.
If your host does not offer this feature, you can install WordPress manually. This involves downloading the latest version from WordPress.org, uploading the files to your server using FTP, creating a MySQL database, and running the installation script. While it sounds technical, WordPress provides detailed instructions and most hosts have support teams that can guide you through it.
Once installed, you can log in to your new site by visiting yourdomain.com/wp-admin. This takes you to the login page where you use the username and password you created during setup. From here, the fun begins. You now have a blank WordPress site waiting for customization.
The installation process only needs to be done once, but it is the gateway to everything that follows. After this, your focus shifts from setup to design, content, and growth.
4. Enter the Dashboard
The Dashboard is your control room. It is the place you will spend most of your time managing and building your site. Once logged in, you are greeted with an overview that shows recent activity, available updates, and shortcuts to common tasks.
The left-hand menu gives you access to everything. Posts and Pages are where you create content. Media stores your images and videos. Appearance is where you manage themes, widgets, and menus. Plugins extend your site’s functionality. Settings control everything from site name to permalink structure.
At first, the Dashboard can feel like a lot to take in, but it is designed to be simple. You do not need to learn everything at once. Focus on creating posts, uploading images, and exploring the Appearance section. As your site grows, you will naturally use more features.
One tip for beginners is to keep the Dashboard clean. Update plugins and themes regularly, delete unused items, and check for notifications. The Dashboard is powerful, but it only works well if you keep it organized. Think of it as the cockpit of your website, where every important control is within reach.
5. Choose a Theme
A theme is the visual identity of your WordPress site. It defines layout, colors, typography, and how visitors move through your content. Choosing the right theme is more than picking something that looks good. It directly affects usability, speed, and search performance. A heavy, bloated theme slows your site and frustrates readers. A lightweight, responsive theme makes pages load quickly and look sharp on any device.
The WordPress theme directory is a great place to start. It offers thousands of free themes that follow WordPress standards. Premium themes often include more advanced features like drag-and-drop page builders or ready-made templates. Before deciding, preview how the theme looks on desktop, tablet, and mobile. Check reviews, update history, and support options.
Think about your site’s purpose. A blog needs a clean layout with strong readability. A business site should highlight services and calls to action. An online store needs WooCommerce compatibility. Start simple, then customize with colors, fonts, and widgets to match your brand. Picking a theme early sets the tone for everything you build afterward.
6. Add Plugins
Plugins are the tools that make WordPress flexible. Out of the box, WordPress gives you a strong foundation, but plugins let you add features like SEO optimization, security, caching, forms, galleries, or even entire online stores. There are over 60,000 free plugins in the WordPress plugin directory plus thousands of premium options.
When adding plugins, less is more. Installing dozens of plugins might seem tempting, but each one adds code that can slow your site. Focus on essentials first. Every new WordPress site should consider an SEO plugin like Yoast or Rank Math, a security plugin like Wordfence, and a caching plugin like WP Super Cache or W3 Total Cache. If you want to sell products, WooCommerce is the go-to plugin. For contact forms, WPForms is simple and reliable.
Before installing, check plugin ratings, number of active installs, and the last update date. A plugin that has not been updated in years might cause conflicts. Choose trusted plugins that are maintained regularly. Start with the basics, then add more only when you truly need them.
7. Create Content
Content is the heart of your WordPress site. It is the reason visitors come and the reason they stay. The WordPress block editor makes writing simple by letting you build posts and pages with blocks. Each block can be text, an image, a video, a gallery, or even a button. You can move blocks around, rearrange sections, and create layouts without touching code.
If you are starting a blog, focus on posts. Use categories and tags to organize them so readers can find related articles. If you are building a business site, start with essential pages such as “About,” “Services,” and “Contact.” Every site also benefits from a homepage that clearly explains what you offer and why it matters.
Visuals are powerful. Add images, infographics, or embedded videos to break up text and make content more engaging. Keep readability in mind. Use headings, short paragraphs, and bullet points to make scanning easy. Finally, think about your audience. Write to answer their questions, solve problems, or entertain. High-quality content is not just good for visitors. It also improves your search rankings and builds long-term trust.
8. Build Menus and Navigation
Navigation is what helps visitors move through your site. Without it, even great content can get lost. WordPress makes building menus straightforward. From the Dashboard, you can create menus using pages, categories, or custom links. Place the main menu in your site’s header so it is visible on every page.
Think carefully about structure. Too many menu items overwhelm visitors. A simple menu with clear labels is easier to use. If you run a blog, consider linking to categories like “Guides,” “News,” and “Reviews.” A business site might highlight “Services,” “Portfolio,” and “Contact.” You can also create drop-down menus for grouping related items.
Secondary menus belong in the footer. These are perfect for links to privacy policies, terms of service, or resource pages. WordPress also allows widgets in sidebars, where you can add search boxes, recent posts, or social links.
Good navigation helps readers find what they need quickly. It also improves SEO because search engines can crawl your content more effectively. A clear menu is like a map that guides visitors through your site without confusion.
9. Configure Essentials
Before you launch, take time to configure the basics. These small settings make your site professional and search-friendly. In the WordPress Dashboard, go to Settings. Start with the site title and tagline. Make sure they match your brand or purpose. Adjust the timezone, language, and date format so everything is accurate.
One of the most important settings is permalinks. By default, WordPress creates long URLs with numbers and symbols. Switch to “Post Name” under Permalink settings. This gives you clean, SEO-friendly URLs like yoursite.com/your-post-title. It is easier for visitors to read and better for search engines.
Check the Reading settings next. You can choose whether your homepage displays your latest posts or a static page. If you are running a blog, showing recent posts makes sense. For a business site, a custom homepage is often better.
Finally, look at Discussion settings if you want comments. Decide whether to allow them and set rules for moderation. These small adjustments take only minutes, but they shape the visitor experience and the way your site appears in search results.
10. Optimize and Launch
Optimization is the final step before launch. A well-optimized site loads quickly, looks good on every device, and is secure. Start with caching. Plugins like WP Super Cache or W3 Total Cache store static versions of your pages, reducing load time for repeat visitors. Next, compress images using a tool like Smush or ShortPixel. Large images are one of the biggest causes of slow websites.
Mobile performance is equally important. Test your site on different screen sizes to make sure text is readable and buttons are easy to tap. Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix show where your site can improve.
Do not forget security. Install an SSL certificate so your site uses HTTPS. This protects data and boosts trust with visitors. Check all your links, proofread content, and confirm that navigation works smoothly.
When everything looks good, it is time to launch. Announce your site on social media, share it with friends, and start creating content regularly. Optimization is not a one-time task. Keep testing and improving as your site grows. With a strong foundation, your WordPress site is ready to reach the world.
Why Your Theme Shapes the Whole Experience
A WordPress theme isn’t just decoration. It defines usability.
- Readability: Clear fonts and spacing keep people reading.
- Navigation: Clean menus improve flow.
- Mobile design: Responsive themes adapt to all screens.
- Accessibility: Accessible themes support screen readers.
- Speed: Lightweight themes load faster.
A Quick Look Back: When WordPress Started
- 2003: WordPress was created by Matt Mullenweg and Mike Little.
- May 27, 2003: The first release, WordPress 0.7, went live.
Which Plan Works Best for Bloggers?
If your main goal is blogging, here’s what to know:
WordPress.com Plans
- Free: For hobby blogging.
- Premium: Best for serious writers.
- Business: Unlocks plugins and advanced SEO.
WordPress.org (Self-Hosted)
The best plan depends on convenience vs. customization. Casual bloggers stick with WordPress.com Premium. Growth-focused bloggers should consider Business or self-hosted.
Why It’s Popular, Why It’s Slow, and What the Future Holds
Why WordPress Is Popular
WordPress has grown into the world’s most widely used website builder for good reason. First, it is open-source and free, which means anyone can download and use it without paying a license fee. That openness has created a massive community of contributors who constantly improve the platform.
Second, the dashboard is easy to use. You do not need to be a developer to publish a blog post, upload photos, or add new pages. Everything is managed through a clean interface that feels familiar, even to beginners.
Third, WordPress is SEO-friendly right out of the box. Search engines understand its structure, and with the help of plugins, you can fine-tune everything from metadata to sitemaps.
Fourth, there is community support everywhere. Thousands of forums, tutorials, and meetups exist to help you troubleshoot problems and learn new skills.
Finally, it scales with you. Start with a personal blog and grow into a business site or even a full e-commerce store. WordPress adapts to your needs at every stage. That flexibility is why companies like TechCrunch, The New Yorker, and Sony Music all run their sites on WordPress.
Why WordPress Can Be Slow
For all its strengths, WordPress sometimes gets a reputation for being slow. The truth is, the platform itself is not the problem. Most performance issues come from how a site is set up.
The biggest culprits are heavy themes with unnecessary code, too many plugins, or large unoptimized images. Weak hosting also plays a role. If your server is overloaded, your site will feel sluggish no matter how well it is designed.
The good news is that these problems are easy to fix. Choosing a lightweight theme, limiting plugins to essentials, compressing images, and upgrading to faster hosting can dramatically improve performance. Adding caching and a content delivery network (CDN) takes it even further.
Some of the biggest names using WordPress, like BBC America and Vogue, keep their sites fast by focusing on optimization. Their success proves that a WordPress site can be lightning quick with the right setup.
Will WordPress Shut Down?
One question that comes up often is whether WordPress could ever shut down. The answer is no. WordPress is not owned by a single company. It is an open-source project supported by the WordPress Foundation, a nonprofit that ensures its long-term survival.
Even if companies built around WordPress changed direction, the software itself would continue because the code is freely available to everyone. The global community of developers and users makes it resilient.
Will WordPress Replace Web Developers?
Another concern is whether WordPress will replace the need for web developers. While the platform allows non-technical users to build sites, it does not eliminate the need for expertise. Developers handle the things that make a site stand out, such as custom themes, advanced functionality, performance tuning, and security hardening.
Even with new AI-powered tools that can generate starter sites, strategy and creativity still require humans. Businesses often need unique designs, integrations with other software, or accessibility improvements that only skilled developers can provide.
Rather than replacing developers, WordPress has created more opportunities for them by powering such a large share of the web. In fact, high-profile sites like Microsoft News and TED Blog rely on developers to keep their platforms customized and optimized.
Important Points
- WordPress works by combining content, themes, and plugins into a complete website.
- Themes influence usability, speed, and accessibility.
- The platform started in 2003 and now powers over 43 percent of the web.
- Bloggers should choose Premium or Business on WordPress.com, or self-host for full control.
- WordPress is not shutting down and will not replace developers. It continues to grow stronger.
Final Word
WordPress succeeds because it blends simplicity with power. It is easy enough for a beginner to use yet flexible enough to support large organizations. If you are starting a blog, building a business site, or carving out your own corner of the internet, WordPress gives you the tools to do it.
Choose the right plan, select a solid theme, stay mindful of speed, and your site can grow with you for years to come. Just look at how brands like Time Magazine, Spotify Newsroom, and Disney use it at scale. If it works for them, it can work for you.